Etherium gas fees
Mempool Archive Quickstart: How to use Blocknative's historical Ethereum mempool data to analyze private transactions, MEV, and OFAs
Ethereum gas fees exist because operating the Ethereum network uses resources in the form of computational power. Participants in the Ethereum network can voluntarily operate the blockchain to earn gas fees, provided that they stake—that is, agree not to trade or sell—their ETH. Current eth gas fees When you enter a transaction to the Ethereum blockchain, you specify a “gas limit.” Gas limit refers to the maximum amount of gas you're willing to consume on a transaction. Complicated transactions involving smart contracts require more computational work, so they require a higher gas limit. The standard transaction fee on Ethereum requires a gas limit of 21,000 gwei.
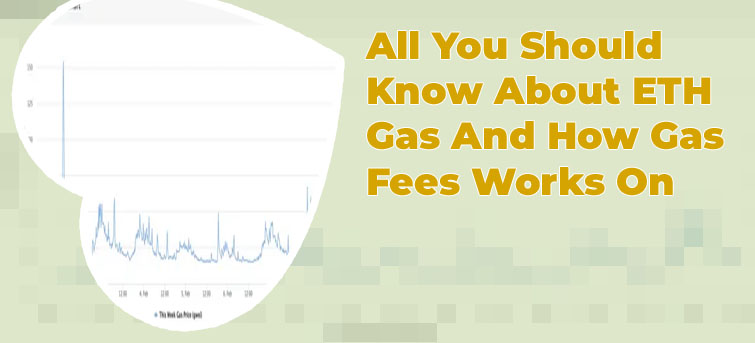
What are eth gas fees right now
Historical data is grouped by hour intervals, and only max fee during this hour per blockchain is used to populate the table below. For Tron, biggest from median gas fees is shown. All fees are shown in USD. Why Do We Need Gas in the Ethereum Ecosystem? Swap from Anywhere, Anytime - with MetaMask
The Merge: Everything You Need to Know
Gas is essentially a measurement of the computational effort needed to execute an operation on Ethereum. More complex operations require more gas to run, while relatively simple transactions like a single token transfer require less gas. Ultimately, “gas” is just another way to measure transaction fees. Gas fees are paid in ETH and are denominated in GWEI. GWEI is just a smaller denomination of ETH, similar to how a penny is a smaller denomination of a dollar. One GWEI is worth 0.000000001 ETH. How Do Ethereum Gas Fees Work? Ethereum’s gas is an essential regulator that prevents anyone from spamming the network. All computation over Ethereum stretches a measure meant to maintain security in place. Gas limits, paid for by each computational execution, help make sure that malicious individuals can’t use unsorted loads of computation power to become de-facto coders on the Ethereum network and hijack the future they helped build together.
Current eth gas fees
Another crucial aspect in discussions about ‘how to calculate Non-fungible tokens gas fee’ would draw the limelight towards gas fee limit. The gas fee limit or gas limit points to the maximum amount of gas you want to spend for a specific transaction. A higher gas limit points out that your transaction would have priority over other transactions with lower gas limits. The flexibility for setting a gas fee limit can help in ensuring that you can exercise a certain level of control over the transaction costs. Gas to Ethereum Data As an investor in the crypto space, it’s important for you to understand how your on-chain transactions are affected by gas fees and why. Today’s article discusses how Ethereum gas fees work, why they’re so high, and how to reduce them.
